Philippine Textiles: A Vibrant Tapestry of Culture and Heritage


Introductioon
Philippine Textiles are a vibrant and integral part of the country’s cultural heritage. These textiles are not just pieces of fabric; they are woven narratives of the Philippines’ rich history, diverse traditions, and the artistry of its people. From the intricate patterns of the T’nalak to the delicate beauty of Piña fabric, each textile tells a unique story that spans centuries. Understanding these textiles involves delving into their historical roots, the various types and techniques of weaving, their cultural significance, and their modern applications and challenges. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a deep dive into the world of Philippine textiles, highlighting their importance and how they continue to evolve today.
The Historical Roots of Philippine Textiles
The history of Philippine textiles is as diverse as the archipelago itself. Long before the arrival of Spanish colonizers, indigenous groups across the islands practiced textile weaving. These early textiles were often used in rituals and ceremonies, reflecting the spiritual and social values of different communities.
With the advent of Spanish colonization in the 16th century, the textile industry experienced significant changes. Spanish influences introduced new techniques and materials, enriching the local weaving traditions. However, it was not just an exchange of techniques but also of cultural and artistic values, which blended to create unique textile patterns and designs.
During the American and Japanese periods in the early 20th century, further innovations were introduced. The American period brought about industrialization, which significantly affected the traditional handloom industry. Despite these challenges, the resilience of local weavers ensured that traditional practices were preserved and passed down through generations.
Diverse Types of Philippine Textiles
Abaca: The Queen of Philippine Fibers
Abaca, known scientifically as Musa textilis, is a type of banana native to the Philippines. This fiber is prized for its strength, flexibility, and natural resistance to saltwater damage, making it ideal for marine use and high-quality textiles. The traditional process of extracting abaca fibers involves harvesting the leaf sheath, scraping off the pulp, and drying the fibers in the sun. These fibers are then woven into various products such as ropes, mats, and fine textiles.
Traditional Methods of Abaca Extraction
The traditional method of extracting abaca fibers is labor-intensive and involves several steps. First, the leaf sheath of the abaca plant is carefully harvested. The outer layers are then removed, revealing the inner fibers. The pulp is scraped off meticulously to ensure the fibers remain intact. Finally, the fibers are sun-dried to enhance their strength and flexibility.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Fiber
Abaca is not only strong and versatile but also sustainable. The cultivation of abaca plants requires minimal chemical inputs, making it an environmentally friendly crop. Additionally, the entire extraction process is natural and does not involve harmful chemicals, ensuring that abaca remains a green and sustainable resource.


Piña: The Pride of the Philippines
Piña fabric is a unique and exquisite textile made from the fibers of pineapple leaves, specifically from the Red Spanish variety. This delicate fabric is celebrated for its silky texture and translucence, making it highly sought after for various high-end applications.
The Labor-Intensive Production Process
The production of piña fabric is labor-intensive and involves several meticulous steps. First, the fibers are hand-extracted from pineapple leaves, a process that requires precision and care. These fibers are then carefully washed and dried. Once prepared, the fibers are knotted together to form long, continuous threads suitable for weaving. This knotting process is delicate and time-consuming, ensuring the final fabric’s strength and uniformity.
Modern Applications and Eco-Friendly Nature
In addition to traditional garments, piña fabric is now being used in various modern applications. It is popular in high-end fashion, home décor, and even accessories such as scarves and handbags. Its eco-friendly nature also makes it a sustainable choice. The production of piña fabric involves minimal chemical use and promotes the recycling of pineapple leaves, which would otherwise be agricultural waste.
T’nalak: The Sacred Weave of the T’boli Tribe
T’nalak is a unique fabric made by the T’boli people living in South Cotabato, Philippines. This fabric is created from abaca fibers, which are dyed with natural pigments obtained from local plants and trees. The weaving process of T’nalak is deeply spiritual and symbolic. The weavers, sometimes called “dream weavers,” draw inspiration for their patterns from their dreams and visions. Each piece of T’nalak is unique, and its patterns reflect various aspects of T’boli culture and beliefs.
The process of creating T’nalak begins with harvesting abaca fibers. These fibers are carefully cleaned, dried, and dyed using natural colors derived from plants. The dyed fibers are then handwoven on a traditional loom. The weavers work meticulously, and it can take months to complete a single piece of T’nalak. The patterns they create are not just decorative; they are symbolic representations of T’boli myths, legends, and spiritual beliefs.
T’nalak is more than just fabric; it is a cultural treasure. It plays an important role in T’boli ceremonies and rituals. For the T’boli people, T’nalak symbolizes the connection between the human world and the spirit world. This fabric is used in various ceremonies, including weddings and other significant events.
T’nalak is also valued for its beauty and durability. Items made from T’nalak can be used in clothing, accessories, and decor. Recently, T’nalak has gained popularity beyond the Philippines, and many people are beginning to appreciate its uniqueness and cultural significance.


Inabel: The Ilocano Weave
Inabel, or Abel Iloco, is a traditional textile from the Ilocos region of the Philippines. It is made from high-quality cotton and is known for its exceptional durability and intricate designs. The weaving process involves using handlooms, a craft that has been passed down through generations of skilled weavers. Each piece of Inabel textile is a testament to the weaver’s artistry and dedication to preserving this cultural heritage.
Inabel textiles are incredibly versatile and can be used in various ways. They are commonly used for traditional and modern clothing, including dresses, skirts, and barongs. Additionally, Inabel fabrics are popular in home décor, serving as beautiful table runners, curtains, and pillowcases. The textiles are also used to create stylish accessories such as bags, scarves, and shawls.
The designs of Inabel textiles often feature intricate geometric patterns and motifs inspired by nature, such as flowers, birds, and other elements of the natural world. These designs are not only aesthetically pleasing but also hold cultural significance, reflecting the traditions and values of the Ilocano people. The vibrant colors and detailed patterns make Inabel textiles a unique and cherished part of Filipino culture.
Through the continued practice of this traditional craft, Inabel weaving helps preserve the rich cultural heritage of the Ilocos region and supports the livelihoods of local weavers. As more people around the world discover the beauty and craftsmanship of Inabel textiles, this ancient art form continues to thrive and evolve.
Traditional Weaving Techniques in the Philippines
The art of weaving in the Philippines is a meticulous process that has been perfected over centuries. Traditional weaving techniques are not just methods of fabric production; they are expressions of cultural identity and craftsmanship that reflect the ingenuity and artistry of the Filipino people.
Handloom Weaving
Handloom weaving is a widespread technique used across the Philippines. It involves the use of a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. This technique allows for the creation of intricate patterns and designs. The process is labor-intensive, requiring significant skill and patience. The resulting textiles are highly valued for their quality and beauty.
Ikat: The Tie-Dye Technique
One of the most fascinating traditional weaving techniques in the Philippines is ikat. This method involves dyeing the yarns before weaving them into fabric. Portions of the yarn are tightly bound to resist dye penetration, creating intricate patterns when woven. Ikat is known for its distinctive, often blurred patterns that give the textiles a unique and artistic appearance. Each region has its own variation of ikat, reflecting local cultural influences and aesthetic preferences.
Backstrap Loom Weaving
Backstrap loom weaving is another traditional technique, particularly prevalent among indigenous communities. This method uses a simple, portable loom where one end is attached to a stationary object and the other to the weaver’s body. The tension is controlled by the weaver leaning back, hence the name “backstrap loom.” This technique allows for greater flexibility and control over the weaving process, enabling the creation of highly detailed and complex designs. It is often used to produce smaller items such as belts, bags, and ceremonial cloths.

Cultural Significance of Philippine Textiles
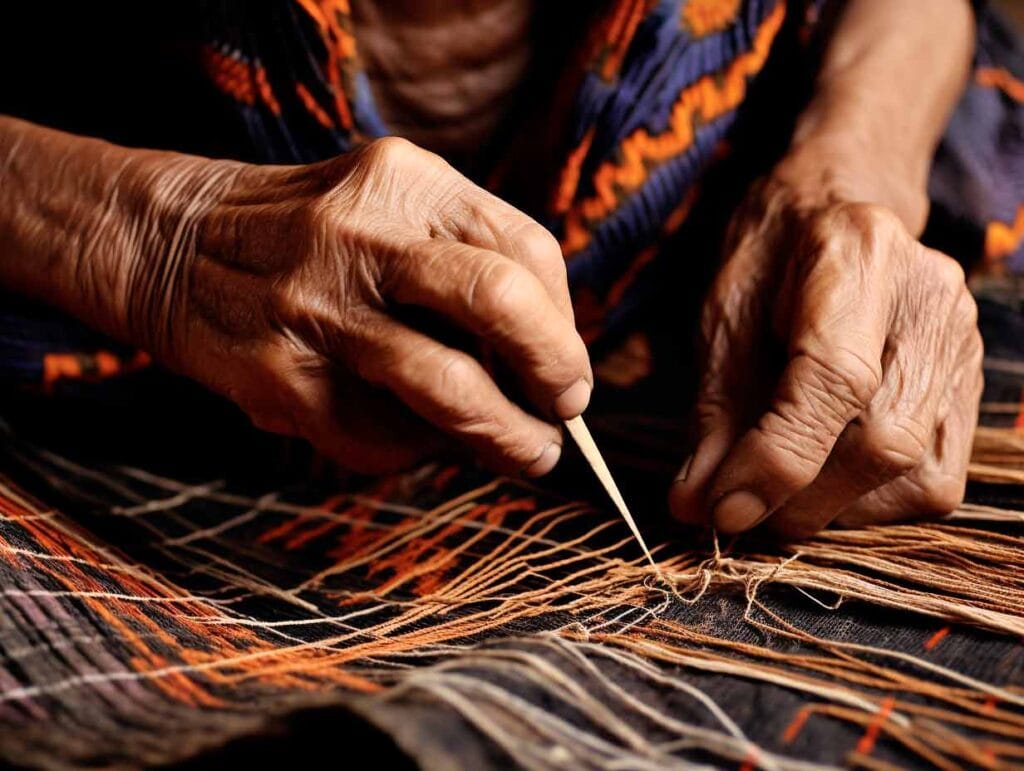

Philippine textiles are deeply intertwined with the cultural and social fabric of the country. They play a crucial role in various aspects of life, from everyday use to significant rituals and ceremonies.
Role in Rituals and Ceremonies
In many Filipino communities, textiles are not merely utilitarian objects but hold profound symbolic meanings. For instance, the T’nalak fabric of the T’boli tribe is used in important life events such as weddings and funerals. It is believed to possess spiritual significance, with patterns often interpreted as messages from ancestors or deities. Similarly, the Inabel fabric is used in religious festivities and traditional celebrations in the Ilocos region, where it symbolizes wealth, status, and artistic heritage.
Symbolism in Patterns and Colors
The patterns and colors in Philippine textiles are laden with symbolism. For example, the intricate designs of the T’nalak often depict the T’boli’s connection to nature and their spiritual beliefs. Red symbolizes bravery and valor, while black and white represent balance and harmony. In Piña textiles, floral and geometric patterns are prevalent, reflecting both the natural environment and the artistic creativity of the weavers.
Preservation of Indigenous Identity
Textiles serve as a means of preserving and expressing indigenous identities. Each piece of fabric tells a story about the community it comes from, including its history, values, and traditions. By continuing to practice traditional weaving, communities maintain a connection to their heritage and pass on these skills and stories to future generations. This preservation is crucial in the face of globalization and cultural homogenization, as it helps sustain the unique cultural diversity of the Philippines.
Modern Applications and Innovations in Philippine Textiles
Philippine textiles have not only survived through centuries but have also evolved, adapting to contemporary needs and innovations. The fusion of traditional techniques with modern applications has opened new avenues for these textiles in both local and global markets.
Philippine Textiles in Contemporary Fashion
One of the most prominent modern applications of Philippine textiles is in the fashion industry. Designers, both local and international, have embraced these textiles for their unique beauty and cultural significance. Piña fabric, for instance, is a favorite in the creation of elegant formal wear such as the Barong Tagalog and wedding gowns. Its lightweight, sheer quality makes it ideal for sophisticated and stylish garments.
Several Filipino designers have gained international acclaim for incorporating traditional textiles into their collections. By blending traditional patterns and materials with modern design sensibilities, they create pieces that are both contemporary and rooted in heritage. This trend not only showcases the versatility of Philippine textiles but also helps promote and preserve these traditional crafts.
Sustainable Practices and Innovations
Sustainability has become a significant focus in the textile industry, and Philippine textiles are no exception. Many artisans and producers are adopting eco-friendly practices to ensure the sustainability of their craft. For example, the production of abaca and piña fabrics involves minimal use of chemicals, relying instead on natural processes. The fibers are biodegradable and sourced from plants that are abundant and renewable.
Innovations in textile production have also led to the development of new materials and methods that reduce environmental impact. Some weavers are experimenting with organic dyes made from local plants and fruits, which are less harmful to the environment compared to synthetic dyes. Additionally, efforts are being made to revive traditional practices that are inherently sustainable, such as using natural fibers and handloom weaving, which have a lower carbon footprint compared to industrial methods.
These sustainable practices not only help in conserving the environment but also ensure that the art of traditional weaving can continue for future generations. By supporting sustainable and ethical production methods, consumers can contribute to the preservation of these cultural heritage practices.
Challenges Facing the Philippine Textile Industry

Despite the rich heritage and growing interest in Philippine textiles, the industry faces several challenges. Economic and social issues, the impact of globalization, and industrialization threaten the survival of traditional weaving practices.
Economic and Social Challenges
Many traditional weavers live in rural areas with limited access to resources and markets. The economic viability of weaving as a profession is often challenged by low wages and competition from mass-produced textiles. Younger generations may be reluctant to continue the craft due to these economic hardships and the lure of better opportunities in urban areas.
Impact of Globalization and Industrialization
Globalization and the rise of fast fashion have significantly impacted traditional textile industries worldwide. Mass-produced, inexpensive fabrics dominate the market, making it difficult for handcrafted textiles to compete. The shift towards industrialized production methods has also led to a decline in the number of traditional weavers and the loss of indigenous knowledge and skills.
Preservation and Promotion Efforts
Despite these challenges, various efforts are being made to preserve and promote Philippine textiles. Government agencies, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and private initiatives are working to support the industry and ensure its sustainability.
Government and NGO Initiatives
The Philippine government, through agencies like the National Commission for Culture and the Arts (NCCA) and the Department of Trade and Industry (DTI), has implemented programs to support traditional weavers. These initiatives include funding for training programs, grants for weaving cooperatives, and marketing assistance to help artisans reach a wider audience.
NGOs also play a crucial role in preserving traditional weaving practices. Organizations such as the HABI Philippine Textile Council work to promote the appreciation and use of indigenous textiles through exhibitions, workshops, and collaborations with designers. These efforts help raise awareness about the cultural significance of Philippine textiles and provide platforms for weavers to showcase their work.
Role of Local Artisans and Communities
Local communities and artisans are at the heart of the preservation efforts. By continuing to practice traditional weaving and passing down their skills to younger generations, they keep their cultural heritage alive. Community-based initiatives, such as weaving cooperatives, provide support and resources to artisans, enabling them to sustain their craft economically.
How You Can Support Philippine Textiles
Supporting the preservation and promotion of Philippine textiles is essential to ensure the survival of these cultural treasures. There are several ways individuals can contribute to this cause, from purchasing authentic products to raising awareness about the importance of traditional weaving.
Buying Authentic Products
One of the most direct ways to support Philippine textiles is by purchasing authentic products. By buying items made from traditional textiles, such as clothing, home décor, and accessories, you contribute to the livelihoods of the artisans who create them. Look for products that are certified or verified as genuine to ensure that your purchase supports the weavers and their communities.
When buying Philippine textiles, consider the following tips:
- Buy Directly from Artisans: Whenever possible, purchase textiles directly from the weavers or through fair trade organizations. This ensures that a fair portion of the proceeds goes to the artisans.
- Support Local Markets and Craft Fairs: Attend local markets, craft fairs, and exhibitions where traditional weavers showcase and sell their work. These events are excellent opportunities to find unique, high-quality textiles.
- Check for Authenticity: Be mindful of imitations and mass-produced items that may not support traditional weaving practices. Look for certifications or labels that verify the authenticity of the textiles.

Supporting the preservation and promotion of Philippine textiles is essential to ensure the survival of these cultural treasures. There are several ways individuals can contribute to this cause, from purchasing authentic products to raising awareness about the importance of traditional weaving.
Supporting Local Weavers and Artisans
In addition to purchasing products, there are other ways to support local weavers and artisans. Donations, volunteer work, and partnerships with organizations that promote traditional weaving can make a significant impact.
- Donate to Organizations: Contribute to NGOs and organizations dedicated to preserving Philippine textiles. Donations help fund programs that provide training, resources, and marketing support to weavers.
- Volunteer Your Time: If you have skills in marketing, design, or business, consider volunteering with organizations that support traditional weavers. Your expertise can help them reach a broader audience and improve their economic prospects.
- Collaborate with Artisans: Designers and businesses can collaborate with local weavers to create unique products that blend traditional techniques with contemporary designs. These partnerships can provide valuable exposure and financial support for the artisans.
Promoting Awareness Through Social Media
Raising awareness about the importance of Philippine textiles is crucial for their preservation. Social media platforms offer powerful tools for spreading the word and engaging a global audience.
- Share Stories and Information: Use social media to share stories about the history, significance, and beauty of Philippine textiles. Highlight the artisans behind the work and the cultural heritage they represent.
- Promote Events and Exhibitions: Help promote events, exhibitions, and craft fairs that showcase traditional textiles. Encourage your followers to attend and support these initiatives.
- Use Hashtags: Utilize relevant hashtags, such as #PhilippineTextiles, #SupportLocal, and #Handwoven, to reach a wider audience and connect with others who are passionate about traditional weaving.
The Future of Philippine Textiles
The future of Philippine textiles hinges on a delicate balance between preservation and innovation. As we have seen, these textiles are not just products but embodiments of the Philippines’ rich cultural heritage and artisanal skill. Preserving traditional weaving techniques and the stories they tell is crucial for maintaining the cultural identity and artistic legacy of the Filipino people.
However, the journey forward also involves embracing modern applications and sustainable practices. By integrating traditional textiles into contemporary fashion and promoting eco-friendly production methods, we can ensure that these crafts remain relevant and sustainable. Supporting local artisans, buying authentic products, and raising awareness about the importance of Philippine textiles are vital steps in this process.
Encouragement for Readers
As a reader, you play a crucial role in the preservation and promotion of Philippine textiles. Every purchase of an authentic textile, every social media post that highlights the beauty and significance of these fabrics, and every effort to support local artisans contribute to a larger movement to keep these traditions alive. By appreciating and supporting Philippine textiles, you are helping to preserve a rich cultural heritage for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions About Philippine Textiles
What are Philippine textiles? Philippine textiles are traditional fabrics created using indigenous weaving techniques. These textiles are made from natural fibers such as abaca, piña, and cotton and are known for their intricate patterns and cultural significance.
How are traditional Philippine textiles made? Traditional Philippine textiles are made using handloom weaving techniques. The process often involves preparing the fibers, dyeing them using natural pigments, and weaving them into fabric using various looms. Each region has its own unique methods and patterns.
Where can I buy authentic Philippine textiles? Authentic Philippine textiles can be purchased directly from local weavers, at craft fairs and markets, through fair trade organizations, and from specialty stores that support traditional artisans. Ensure the authenticity of the products by checking for certifications or labels.
How can I help preserve Philippine textile traditions? You can help preserve Philippine textile traditions by buying authentic products, supporting local artisans through donations and volunteer work, promoting awareness through social media, and encouraging collaborations between designers and traditional weavers.
